A growing body of research confirms that Vitamin D is necessary for normal bone mineralization and growth, maintenance of muscle strength and coordination, cardiovascular health, and a strong and balanced immune system.
What’s unique about this vitamin is that it works like a hormone in our DNA. It is estimated that vitamin D regulates between 200-300 genes which explains why it directly affects good health.
Vitamin D And Your Body
:: Promotes a healthy, balanced immune system through regulation and differentiation of immune system cells.
:: Supports the development and maintenance of bones and teeth by helping with the absorption and use of calcium.
:: Minimizes age-associated bone loss.
:: Lowers risk of MS, arteriosclerosis, breast cancer, bowel cancer
:: Absorbs into the skin through sunlight exposure. The more skin you expose, the more vitamin D will be produced.
Immune System Health
Did you know that vitamin D promotes a healthy, balanced immune system? It has also been linked to improved cardiovascular health and helps maintain normal functioning of the nervous system.
This important little vitamin does a lot of work in keeping lungs healthy, helping the elderly maintain lean muscle mass, and maintaining healthy bones and teeth. All of this is due to vitamin D’s relationship with calcium.
Calcium
Calcium is the major structural element of bones and teeth. Your body needs several nutrients in order for calcium to be absorbed and used properly. Two of these nutrients are vitamin D and vitamin K.
Vitamin D increases absorption of calcium from the small intestine so the body receives maximum benefit, while vitamin K helps make sure calcium builds up in the bones and not in soft tissues. Adequate calcium and vitamin D throughout life may reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
Natural Sources of vitamin D
Food
Since there is only a small amount of vitamin D found in a few foods, it’s nearly impossible to get what you need from food alone. The best food sources of vitamin D include fatty fish, egg yolks, orange juice, and some cereals.
The Sun
When bare skin is exposed to direct sunlight, ultraviolet B (UVB) rays produce vitamin D3. The challenge is that too much sun can be bad for your skin.
You absorb different amounts of vitamin D from sunlight depending on the time of day and year, where you live, and the color of your skin. Winter sunlight doesn’t produce the same amount of vitamin D that summer sunshine does.
Vitamin D Deficiency
It is currently estimated that more than 1 billion people worldwide and 30-to-40% of the population between 15 and 49 years of age in the U.S. suffer from vitamin D deficiency.
The cells in your body have vitamin D receptors that require vitamin D to function properly, including those in your skin and brain.
Signs You May Be Vitamin D Deficient
Painful Joints
Calcium and phosphorus are necessary for developing a the strength of your bones, and these minerals are best absorbed with vitamin D.
Tummy Problems
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin. Certain gut conditions can lower your absorption of vitamin D.
Feeling Depressed
Serotonin is a hormone that affects mood. Our brains produce serotonin at a higher rate when we’re exposed to sunshine or bright light, a main source of vitamin D.
Age
As we age, our skin loses its ability to absorb as much vitamin D. Our kidneys also slowly become less effective at converting vitamin D in our body.
Excessive Weight
Vitamin D is collected and stored in fatty tissue. If you’re overweight, you need more vitamin D than someone with a lower percentage of body fat for optimal results.
Skin Color
Some research suggests that those with darker skin may need up to 10 times more sun exposure than those with lighter skin to produce enough vitamin D.
Sweat
Excessive sweating (notably on your forehead) is a very common symptom of vitamin D deficiency. A simple blood test can check your vitamin D levels.
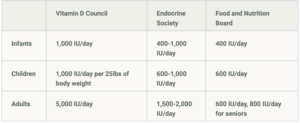
How Much Vitamin D is Enough?
Everyone has different needs, as shown above. To determine if you have adequate Vitamin D levels, get tested by your doctor or go to https://grassrootshealth.net/project/daction/ for a home test. See the chart below for recomendations from the Vitamin D Council.
Vitamin D supplements have the potential to interact with certain types of medications (including steroids and cholesterol-lowering drugs). Those taking medications should discuss vitamin D supplementation with their healthcare providers prior to use.
It’s important to find a supplement that you can trust. The one I use is found here. It’s formulated with a high level of vitamin D to help prevent deficiency by ensuring you get adequate amounts throughout the entire year. It’s also formulated with a potency guarantee of what’s on the label is in the bottle.
Want more healthy lifestyle tips and tasty nutritious recipes? Subscribe here to get them fresh off the press straight to your inbox.
Blessings,
Sheila

